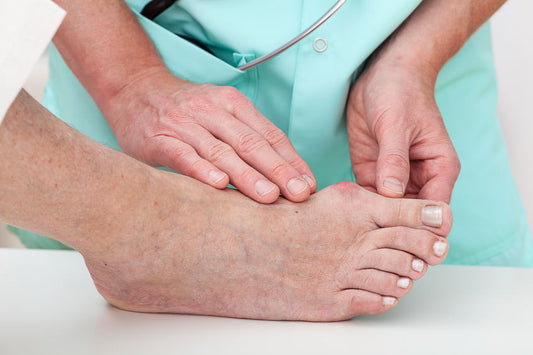
Symptoms
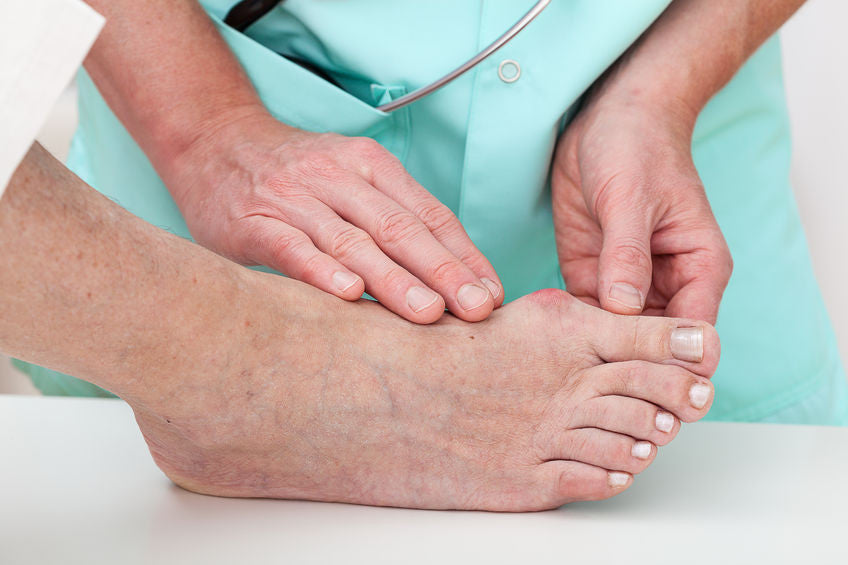
- Painful area around the big toe joint which may be red and swollen
- The big toe may be stiff and not want to bend and may be painful
Definitions
- An inflammation of the big toe joint that may cause an enlargement
- A bony protrusion, which is also generally associated with the angling of the big toe toward the smaller toes creating pressure at the first joint of the big toe.
Primary Cause
Heredity
- Generally one does not have a choice if they develop a bunion.
- If there is not enough arch support or support under the ball of the foot the bunion can become worse
Excessive Pronation
- Pronation is a normal movement of the foot that allows the arch to flatten to a degree, which helps the body to absorb shock and adapt to different ground surfaces.
- In analyzing ones gait, first contact is on the heel and outside of the foot; followed by a shift of body weight continuing forward, toward the arch and toes.
- If the foot is weak or tired and/or the footwear is not supportive, then the arch can flatten more than normal, which is excessive pronation.
- Flattening of the arch (excessive pronation) places pressure and excessive force on the big toe joint which can cause degenerative changes and inflammation that can irritate the bunion.
- With excessive pronation, increased stresses can be placed on the foot which can further contribute to ankle, knee, hip and low back problems (a chain reaction)
Contributing Factors
- Wearing shoes that do not fit correctly - such as narrow shoes or shoes with pointed toes
- Incorrect foot mechanics – excessive pronation
- Injury or arthritis may eventually increase the bunion.
- Wearing high heeled shoes with pointed or narrow toe box
- Insufficient support in the platform (and/or the inside arch area) of the shoe being worn can add to the stress on the foot (bunion).
Treatment - Advice Given Most In Current Literature
The 3 S’s — Stretching, Strengthening and Supporting, along with ICE and REST, have been found to be the simplest and most effective in treating these problems.
- Stretching of the calf and foot will help to decrease the pressure on the foot.
- Strengthening the ankle and foot, can help reduce pressures on the foot due to over pronation.
- Supporting the foot with proper shoes and insoles, can prevent or eliminate the vast majority of foot related problems. Although bunions and hallux valgus are hereditary, the symptoms can be kept to a minimum by reducing the pressure. This can be done by a Birkenstock sandal, with a broad base and contoured foot bed, that is low to the ground and conforms to the foot. It may also be a shoe with an upper that wraps the foot and supports the arch and heel, thus limiting excessive pronation. The vast majority of footwear have more than enough cushion but very little support for the arch and heel. Finding a shoe with extra depth and wide toe box can be very important. One of the easiest and most effective solutions is to add a simple over the counter insole that provides a forgiving support for both the arch and heel. We offer shoe inserts for Bunionettes to help minimize the pain.
- Wear shoes with a wider toe box
- Stretching of the calf, achilles tendon and foot